Arranging Widgets
You can make your GUIs as simple or as complicated as you want...
Sequential Layout
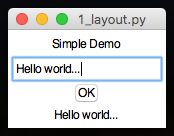
By default, each time you add a widget to a GUI, it is simply added on a new row:
from appJar import gui
def changeLabel(btn):
app.setLabel("l2", app.getEntry("text"))
app = gui()
app.addLabel("l1", "Simple Demo")
app.addEntry("text")
app.addButton("OK", changeLabel)
app.addEmptyLabel("l2")
app.go()
Grid Layout
If, however, you want a bit more control, then you can treat your GUI like a GRID.
Think of it just like a spreadsheet, and position your widgets in whichever cell you want.
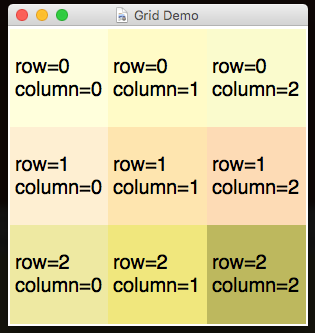
Each time you add a widget, simply specify the row and column it should appear in (always in that order):
from appJar import gui
app=gui("Grid Demo", "300x300")
app.setSticky("news")
app.setExpand("both")
app.setFont(20)
app.addLabel("l1", "row=0\ncolumn=0", 0, 0)
app.addLabel("l2", "row=0\ncolumn=1", 0, 1)
app.addLabel("l3", "row=0\ncolumn=2", 0, 2)
app.addLabel("l4", "row=1\ncolumn=0", 1, 0)
app.addLabel("l5", "row=1\ncolumn=1", 1, 1)
app.addLabel("l6", "row=1\ncolumn=2", 1, 2)
app.addLabel("l7", "row=2\ncolumn=0", 2, 0)
app.addLabel("l8", "row=2\ncolumn=1", 2, 1)
app.addLabel("l9", "row=2\ncolumn=2", 2, 2)
app.setLabelBg("l1", "LightYellow")
app.setLabelBg("l2", "LemonChiffon")
app.setLabelBg("l3", "LightGoldenRodYellow")
app.setLabelBg("l4", "PapayaWhip")
app.setLabelBg("l5", "Moccasin")
app.setLabelBg("l6", "PeachPuff")
app.setLabelBg("l7", "PaleGoldenRod")
app.setLabelBg("l8", "Khaki")
app.setLabelBg("l9", "DarkKhaki")
app.go()
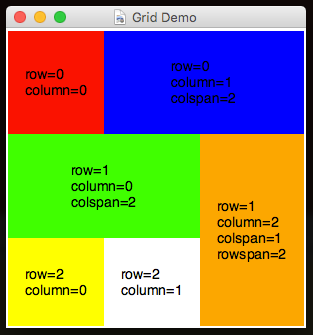
If you're still not satisfied, you can configure widgets to span across multiple columns or rows.
Simply provide a third & fourth parameter to specify how many rows and columns to span:
from appJar import gui
app=gui("Grid Demo", "300x300")
app.setSticky("news")
app.setExpand("both")
app.setFont(14)
app.addLabel("l1", "row=0\ncolumn=0")
app.addLabel("l2", "row=0\ncolumn=1\ncolspan=2", 0, 1, 2)
app.addLabel("l4", "row=1\ncolumn=0\ncolspan=2", 1, 0, 2)
app.addLabel("l6", "row=1\ncolumn=2\ncolspan=1\nrowspan=2", 1, 2, 1, 2)
app.addLabel("l7", "row=2\ncolumn=0", 2)
app.addLabel("l8", "row=2\ncolumn=1", 2, 1)
app.setLabelBg("l1", "red")
app.setLabelBg("l2", "blue")
app.setLabelBg("l4", "green")
app.setLabelBg("l6", "orange")
app.setLabelBg("l7", "yellow")
app.go()
Note, the parameters are read from left to right, so:
- If you're specifying a column, you must first specify a row
- If you're specifying a row-span, you must first specify both the row & column
- And, if you're specifying a column-span, you must first specify a row, column & column-span
Layout Tricks
There are a few tricks you can employ, to make life a bit easier...
Named Arguments
It can be annoying having to specify all of the positional parameters each time, so why not take advantage of Python's support for Named Arguments. These allow you to set specific parameters, using their name.
For example: app.addLabel("l1", "text here", colspan=2), will set the colspan parameter, without having to set the preceding ones.
Row Helpers
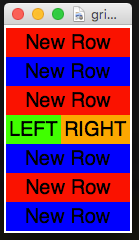
appJar tracks the next available row.:
.getRow()or.gr()
Returns the next free row.
Useful if you're mainly adding things sequentially, but want to modify one line out of sequence.
from appJar import gui
colours=["red","blue"]
app=gui()
for loop in range(3):
app.addLabel(loop, "New Row", colspan=2)
app.setLabelBg(loop, colours[loop%2])
row = app.getRow() # get current row
app.addLabel("a", "LEFT", row, 0)
app.addLabel("b", "RIGHT", row, 1)
app.setLabelBg("a", "green")
app.setLabelBg("b", "orange")
for loop in range(3, 6):
app.addLabel(loop, "New Row", colspan=2)
app.setLabelBg(loop, colours[loop%2])
app.go()
Instead of calling .getRow(), you can specify the string "previous" or "p" to use the the previous row:
from appJar import gui
with gui("LABS", "400x400", sticky="news") as app:
app.label("0-0", bg="red")
app.label("0-1", bg="orange", row="previous", column=1)
app.label("0-2", bg="yellow", row="previous", column=2)
app.label("1-0", bg="green")
app.label("1-1-2", bg="blue", row="previous", column=1, colspan=2)
Widget Positioning
Once you've laid out your widgets, the next most important thing is how they fill the space in their rows and columns.
NB. These settings only take affect from the point at which they are set, so:
- If you want them to affect the whole GUI, set them at the start.
- If you want different settings for different groups of widgets, you'll need to set them before each group.
- If you want different settigs for every widget, you'll need to set them before every widget!
There are two settings you can configure:
- How columns and rows stretch to fill the GUI - stretchiness
- How widgets stretch to fill their cells - stickiness
Setting Stretchiness
.setStretch(sides)
This tells rows & columns how to stretch to fill the GUI, especially when the GUI is resized.
It allows them to adjust to fill the available space:none- don't stretchrow- only rows will stretch (down the GUI)column- only columns will stretch (across the GUI)both- rows & columns will stretch across and and down
By default:
- Columns stretch to fill the width of the GUI
- Rows don't, they take up the minimum space required
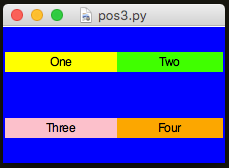
It's possible to tell the rows to stretch too:
app.setStretch("both")
But, as you can see below - this doesn't make any difference (yet).
Even though the rows have stretched down the GUI to fill the space, the widgets inside them aren't sticking to all sides.

Setting Stickiness
.setSticky(sides)
This determines which sides of a grid-cell a widget will stick to.
It should be a string, made up of any combination ofn,e,sorw
By default, most widgets use'ew'- the stick to the sides, but not the top/bottom.
Even if the cells in the columns & rows are stretching (see above), the widgets inside them might not.
Widgets have a stickiness which tells them which sides of their cells to stick to.
By default, widgets are configured to stick to the left & right sides (ew), but not the top & bottom (ns).
To change this, you need to set a new stickiness:
app.setStretch("both")
app.setSticky("nesw")
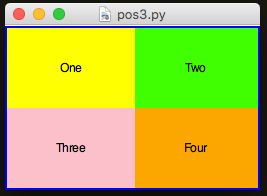
If you remove all stickiness:
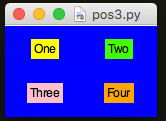
app.setStretch("both")
app.setSticky("")
You end up with:
And, remember, it's possible to give each widget its own stickiness:
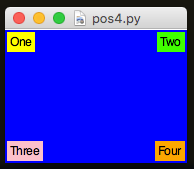
from appJar import gui
app=gui()
app.setBg("blue")
app.setStretch("both")
app.setSticky("nw") #top-right
app.addLabel("l1", "One", 0, 0)
app.setLabelBg("l1", "yellow")
app.setSticky("ne") #top-left
app.addLabel("l2", "Two", 0, 1)
app.setLabelBg("l2", "green")
app.setSticky("sw") #bottom-left
app.addLabel("l3", "Three", 1, 0)
app.setLabelBg("l3", "pink")
app.setSticky("se") # bottom-right
app.addLabel("l4", "Four", 1, 1)
app.setLabelBg("l4", "Orange")
app.go()
NB There is a function to modify an individual widget's stickiness
Examples
You may want two widgets - one filling most of the GUI space, and a second one at the bottom, taking up minimal space:
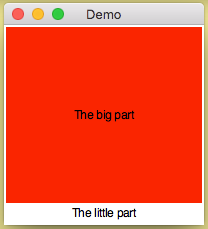
from appJar import gui
with gui('Demo', '200x200') as app:
app.setStretch('both')
app.setSticky('news')
app.addLabel('top', 'The big part')
app.setLabelBg('top', 'red')
app.setStretch('column')
app.setSticky('esw')
app.addLabel('bottom', 'The little part')
NB. This can be achieved in much less code, using the new 1.0 syntax:
from appJar import gui
# set stretch & sticky for the whole GUI
with gui('Demo', '200x200', stretch='both', sticky='news') as app:
app.label('The big part', bg='red')
# change stretch & sticky from this widget on
app.label('The little part', stretch='column', sticky='esw')
Widget Padding
It's possible to configure how much empty space is around a widget.
This is known as padding. You can put padding both inside and outside a widget...
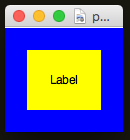
app.setPadding([20,20]) # 20 pixels padding outside the widget [X, Y]
app.setInPadding([20,20]) # 20 pixels padding inside the widget [X, Y]
Set Padding & InPadding
.setPadding([x,y])This sets the X & Y padding outside a widget..setInPadding([x,y])This sets the X & Y padding inside a widget.
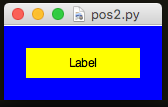
app.setPadding([20,20]) # padding outside the widget
app.setInPadding([40,20]) # padding inside the widget