Algorithms
Below are some comparisons of how to achieve the same thing in a flowchart, pseudocode & Python.
This site was originally written using AQA suggested pseudocode, but will be updated to include OCR recommendations.
It will aso be extended, to include a lot more examples.
Comparison
| Topic | FlowChart | PseudoCode | Python |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assigning a variable | 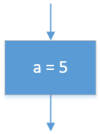 |
a ← 5 | a = 5 |
| Input | 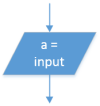 |
a ← USERINPUT | a = input() |
| Output | 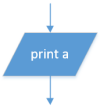 |
OUTPUT a | print(a) |
| Subtraction | 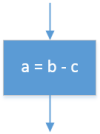 |
a ← b - c | a = b - c |
| Selection: Greater than |
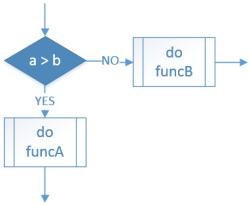 |
IF a > b THEN funcA() ELSE funcB() ENDIF |
if a > b: funcA() else: funcB() |
| Selection: Less than |
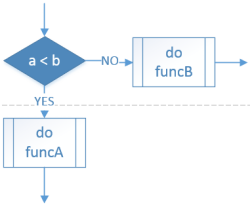 |
IF a < b THEN funcA() ELSE funcB() ENDIF |
if a < b: funcA() else: funcB() |
| Selection: Equal to |
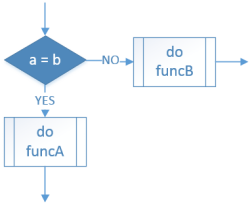 |
IF a = b THEN funcA() ELSE funcB() ENDIF |
if a == b: funcA() else: funcB() |
| Selection: Not equal to |
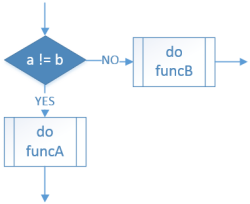 |
IF a ≠ b THEN funcA() ELSE funcB() ENDIF |
if a != b: funcA() else: funcB() |
| Iteration: While loop |
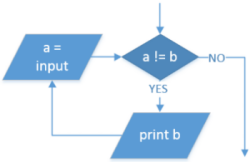 |
WHILE a ≠ b OUTPUT b a ← USERINPUT ENDWHILE |
while a != b: print(b) a = input() |
| Iteration: For loop (count-up) |
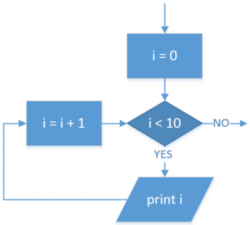 |
FOR i ← 0 TO 9 OUTPUT i ENDFOR |
for i in range(10): print(i) |
| Iteration: For loop (count-down) |
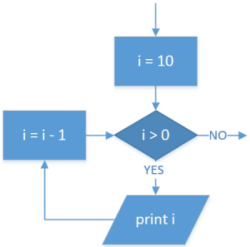 |
FOR i ← 10 TO 1 OUTPUT i ENDFOR |
for i in range(10, 0, -1): print(i) |
Links
Some useful Pseudocode links.